
Bluetooth for IoT
Bluetooth® is a wireless personal area network (PAN) protocol designed for communicating over relatively short distances, (up to a kilometer in some cases) depending on factors such as receiver sensitivity, transmission power and antenna gain. It operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency range, which is license-free, globally.
Bluetooth technology was originally created to replace the RS-232 data cables needed to connect personal computers and cell phones to their accessories and peripherals, such as speakers, headsets and keyboards. Yet it has grown beyond anyone’s wildest imagination to support a vast range of use cases from mobile POS systems to wearables to traffic management and industrial applications.
A Brief History of Bluetooth
Bluetooth began in 1998 with the launch of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), a not-for-profit trade association that grew out of a partnership between five companies: Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia, and Toshiba. The first commercial product was introduced a year later. Thanks to its convenience, flexibility and low-cost, Bluetooth quickly grew in popularity and has become almost universally available in consumer products such as mobile phones and laptops. It’s also a standard feature in virtually all new cars, to support in-vehicle infotainment systems and enable hands-free calling for drivers.
SIG has grown from the original group of five to more than 35,000 member companies worldwide, coming from industries such as telecommunications, computing, networking and consumer electronics. The organization is based in Kirkland, Washington.
Bluetooth Technology Today
After gaining widespread acceptance in consumer markets, newer Bluetooth protocols have enabled the technology to assume a major role in the Internet of Things (IoT). Digi development platforms support Bluetooth to ensure developers can integrate this technology into their designs with ease. For example, the Digi ConnectCore® family of system-on-modules comes pre-certified for Bluetooth connectivity. The Digi XBee® Mobile SDK helps customers design Bluetooth applications that interact with Digi XBee 3 modules.
Bluetooth is now available in three different protocols, each of which is optimal for certain use cases. And while Bluetooth was originally designed for short range use, the latest versions are capable of transmitting signals up to a mile. The three currently available protocols are: Bluetooth Classic, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Bluetooth Mesh.
Bluetooth Classic Use Cases and Application Examples
The Bluetooth Classic protocol is designed for devices that can be recharged on a daily or weekly basis, making it best suited to networks that are limited in size. It is designed to stream high-throughput data at up to 2.1 Mbps over short distances. Having been initially designed to replace short-range peripheral cables, Bluetooth Classic is generally not scalable for IoT applications like sensor networks hosting hundreds of devices.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Use Cases and Application Examples
Bluetooth Low Energy (originally called Bluetooth Smart) supports low-bandwidth connections over short distances in applications that don’t need to handle large data streams, and where batteries may have to last months or even years. BLE is constantly being updated. Now at Bluetooth 5.0, BLE is one of the most ubiquitous wireless protocols in use worldwide today.
Bluetooth Low Energy devices can be run off small coin batteries, making BLE a good choice for devices that transmit only small amounts of data and need to run unattended for extended periods of time. This functionality supports a range of medical devices, wearables and implantables, such as hearing aids and defibrillators.

BLE is also a popular choice for applications such as location beacons, digital scales, temperature monitors, lighting controllers, and other low-bandwidth battery-operated applications, as well as for consumer products including home appliances, fitness monitors, smart watches and TV set-top box remote controls. Beaconing in BLE is designed to support indoor positioning systems that can help people determine their location inside a retail store, mall or other building, as well as for monitoring system performance and tolerance thresholds.
BLE devices and chips can be highly cost-effective. As a point-to-point protocol, the physical size of networks is limited to the traditional Bluetooth range of about 30 feet, although this metric varies widely based on factors discussed earlier. (An excellent discussion of the variables affecting Bluetooth range can be found on the Bluetooth website.) However, BLE has much lower bandwidth capacity than Bluetooth Classic, making it unsuitable for the volume of data involved in media streaming.
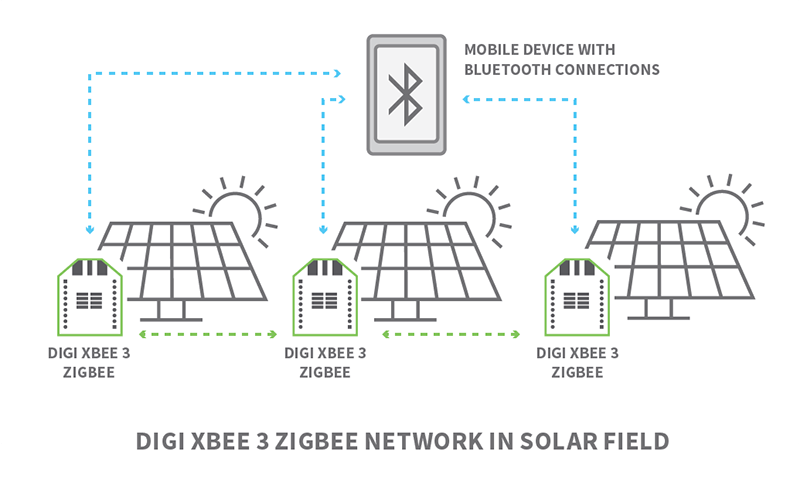
Digi development solutions that provide support for Bluetooth Low Energy include Digi ConnectCore 6UL, Digi ConnectCore 8X and Digi ConnectCore 8M Nano modules. Additionally, Digi XBee 3 modules integrate BLE as a wireless connectivity option for developers wanting to connect their applications to mobile devices, enabling the use of a phone or tablet to set up and test wireless networks.
Bluetooth Mesh Use Cases and Application Examples
Bluetooth Mesh (BT Mesh), which was launched in 2017, extends point-to-point BLE to create mesh networks where nodes act as relays to extend the network beyond the range of any one device. Networks formed as a mesh can forward and route messages to destinations well beyond their nominal range, forming very large physical networks that can scale to include hundreds of devices. The networks are self-forming and self-healing, with sleep support for end devices in a store-and-forward parent/child relationship similar to Zigbee. Bluetooth Mesh also offers low-cost, low-energy use and good security.
Bluetooth Mesh networks are capable of controlling, monitoring, and automating hundreds of connected devices for managing smart buildings and a range of other industrial IoT (IIoT) applications. Bluetooth Mesh was initially designed for the lighting market and because the router nodes need to be powered continuously, lighting is an excellent application, since most lights have access to full-time power. Sensor networks can also be supported by Bluetooth Mesh, but the sensors themselves need to be implemented where full-time power is available.
Bluetooth for IoT Applications
Bluetooth in its different flavors is now being used in a diverse and growing variety of IoT applications. Here are examples of the many use cases for Bluetooth.
- Asset tracking and location services: Real-time location service (RTLS) solutions are used for tracking assets and people, whether it’s pinpointing the location of equipment and workers in a factory or warehouse, or medical devices and staff in a hospital.
- Building automation: Wireless Bluetooth connectivity in the centralized automation of essential building systems — including lighting, security, and heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) — can help conserve energy, lower operating costs, and extend the lifespan of a building’s core systems.
- Condition monitoring: Sensor networks deployed at scale across a factory floor enable real-time monitoring of system performance to reduce maintenance, improve application updating, and increase overall operating efficiency.
- Tank monitoring: Bluetooth connectivity is useful for critical notifications, such as in tank and valve monitoring applications that employ devices like Digi Connect® Sensor+. It provides local installers, technicians or drivers instant feedback from sensor values over Bluetooth.
- Intelligent Traffic Management Systems (ITS): Bluetooth devices detected in passing vehicles can provide information such as the number and speed of vehicles on the road to support applications like real-time highway signage updates, adaptive traffic control, and routing of emergency vehicles. “Bluetooth scanning” for these applications can be performed by the Digi TX54 and Digi TX64 routers. In addition, routers with Bluetooth capabilities can provide connectivity and data communications for traffic system maintenance crews.
- Medical applications: Wireless Bluetooth capabilities for patient monitoring and diagnostics make critical information immediately available to caregivers and medical staff. Medical use cases include wearable devices to help diagnose conditions, administer medication and transmit patient information.
- Contact tracing: The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated that technology can assist in stopping viral spread. Bluetooth can support accurate contact tracing to track, record and send data in real time for rapid response.
- Rideshare and rental applications: Employees who monitor and maintain rental bicycles and scooters in cities or resort areas can use Bluetooth applications out in the field to check on batteries and other systems. City bike and scooter rentals are another use case, using Digi XBee Cellular LTE-M/NB-IoT devices with Bluetooth beaconing.
- Solar and wind farms: Most solar or wind farm installations include radio modules attached to each solar panel or turbine. Using Bluetooth, technicians can take readings to assess current values, productivity or need for service.
- Ticket validation systems: Sporting events, concerts and other events with large crowds can use Bluetooth-equipped readers to validate tickets with barcodes or QR codes.
- Wayfinding: Bluetooth indoor positioning systems (IPS) have quickly become the standard for overcoming the indoor coverage challenges of GPS, helping visitors navigate their way through large public spaces, from airports and train stations to museums and sports stadiums.
Building Bluetooth Apps with the Digi XBee Mobile SDK
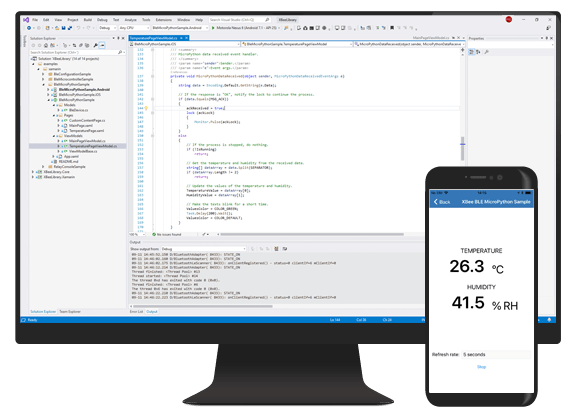
The Digi XBee 3 Series of cellular modems includes integrated Bluetooth Low Energy for local configuration and control via mobile devices. Digi offers the Digi XBee Mobile SDK (Software Development Kit) to help engineers speed the design and development of Bluetooth applications using XBee. The Digi XBee Mobile SDK is a set of libraries, code examples and documentation that helps simplify the process of creating iOS and Android mobile apps that interact with Digi XBee 3 modules via Bluetooth.
Adding Bluetooth to an IoT application adds tremendous value to commissioning, configuration and troubleshooting a network. But creating a mobile app to integrate an IoT application and mobile device can be tricky, with complex authentication and encryption involved in the design of a Bluetooth-enabled mobile app. The Digi XBee Mobile SDK provides the support to simplify and expedite these processes.
Bluetooth Growth and Future Opportunities
Bluetooth technology is expected to ship annually in more than 6 billion devices by 2025, according to the 2021 Bluetooth Market Update from the Bluetooth SIG. The report states that the key Bluetooth use cases and market needs today include audio streaming, data transfer, location services and device networks. Additionally, the organization predicts:
- 10% CAGR between 2021 and 2025
- 70% of Bluetooth enabled devices in 2025 will be peripherals
- 3x growth in annual shipments of single-mode Bluetooth LE devices from 2021 through 2025
Any organization that designs, builds or benefits from wireless connectivity in the IoT needs to include Bluetooth in its short-term and long-term planning. Granted, Bluetooth is only one of several wireless technologies on the market. Yet with so many industries taking advantage of its strengths — such as cost effectiveness, security and ease-of-use — it’s important for every organization to evaluate potential use cases for Bluetooth integration to drive new functionality and ROI.
Contact Digi today to discuss where Bluetooth belongs in your next IoT project, or get design and development support to take your idea to market.