The Internet of Things is in every business and government sector today, from industrial applications to emergency services, public transportation and mobility, public safety, city lighting and other smart city applications.
Due to IoT technology advancements, municipalities are becoming more and more connected in an effort to increase the efficiency of infrastructure installations, improve reliability and responsiveness of emergency services, cut costs and more. And innovation is ongoing. We expect to see many more smart city ideas using IoT solutions for this market in the years to come.
In this post we will look at a few examples of IoT solutions across the smart cities landscape and the benefits cities are experiencing as a result of implementing them.
Key Drivers for IoT Applications in Smart Cities
There are several reasons for municipalities to move to the wireless communications methods offered by IoT technologies.
- Cost is a key driver in the decision to convert from wired solutions to wireless, as it is massively expensive to install and maintain landlines. Additionally, the costs of cellular data plans are dropping and the robustness and throughput of wireless communications are therefore enabling new use cases that would previously have been cost-prohibitive.
- Efficiency is another important impetus. In most wired solutions, service personnel must physically go to the installation site to audit and service the communications infrastructure. These "truck rolls" are expensive and inefficient, since they typically occur on a schedule whether or not a problem exists. By contrast, wireless communications enable remote monitoring and management of IoT deployments. This enables administrators to perform firmware updates and security patches across the entire deployment, and get automated notifications in the event of any issues.
- Resource reduction is often a driver as well, particularly in use cases such as smart street lighting and monitoring assets. These IoT applications make it possible to use sensors to gather data and wireless modules to control resource use, which can result in a dramatic reduction in energy use.
Examples of IoT Applications for Smart Cities
This industry is growing so rapidly that it is a difficult undertaking to capture the breadth of applications in this industry. In fact, "smart cities" could be considered a collection of industries that includes city lighting, city transit, waste water management, emergency services, traffic management and more. In fact, new IoT smart city projects are likely to emerge as the available technologies become more widely adopted, and more targeted at the requirements of specific use cases. We will cover city lighting, public transportation, and water management.
City Lighting Applications
Lighting is one of the most prevalent examples of IoT applications for smart cities, and many municipalities today are turning to wireless communications for cost savings and energy reduction.
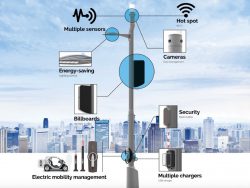
Digi Remote Manager®, a centralized software platform with a graphical user interface.
The solution incorporates the ruggedized
Digi WR44R enterprise class router, which provides connectivity and data routing for multiple device nodes on the Smart Pole. The result is a comprehensive application supporting multiple uses:
- LED lighting controls
- Surveillance cameras
- Environmental sensors
- Electronic billboards
- Charging stations
- Wi-Fi coverage
City Transit Applications

Transit systems are another rapidly growing segment for smart city IoT applications. Transit agencies and smart cities are realizing enormous benefits in cost reduction, safety, routing management and improved rider experience. Where many municipalities saw ridership dropping in recent years, many are now experiencing renewed growth with improved visibility into bus and light rail routing and passenger Wi-Fi connectivity.
For an excellent example, we turn to
SMART, the Suburban Mobility Authority for Rapid Transit Authority, which operates a fleet of more than 330 biodiesel and hybrid-electric buses across Michigans Macomb, Oakland, and Wayne Counties. The IoT solution deployed by the SMART transit system includes a range of features, which are enabled by the
Digi WR44 R industrial router:
- Upgraded Automatic Vehicle Location (AVL) system, with two-way communications between the vehicles and SMARTs dispatch center. This upgrade involved moving from an outdated analog network to cellular communication with voice over IP (VoIP).
- Onboard communications and passenger Wi-Fi, with priority access managed by
- Secure fare collection and mobile ticketing, via the WR44 Rs stateful firewall, IPSec VPN, network segmentation and authentication.
- Network and system monitoring and maintenance, including mass updates and fleet monitoring, via Digi Remote Manager®.These enhancements help transit employees, dispatchers and riders to experience more reliable connectivity and improved communications. Additionally, with the increase in eco-friendly vehicles, smart cities can achieve air quality. This goal as well as reduced congestion are further enhanced with improved ridership and fewer city residents jumping into a car each time they need to travel across town.
Read more about smart city IoT applications for busing and light rail in our customer stories.
Environmental and Wastewater Management Applications
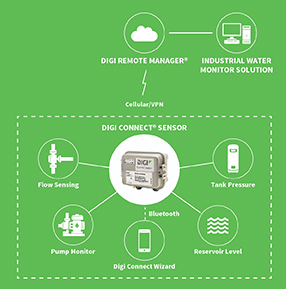
Water management application needs for smart cities run the gamut from wastewater treatment to water monitoring to environmental restoration projects.
IoT applications are growing in these segments as governmental organizations and local municipalities seek to upgrade aging infrastructure, increase efficiency, improve visibility into remote tanks and water management processes, and reduce the cost of monitoring and servicing their assets. While there may not be a "typical" solution, as each of the use cases mentioned above has its own requirements, its useful to look at the components of a sample application.
This particular example shows how a gateway supplies the connectivity for a range of application needs, such as sensing flow rates, tank pressure and water levels.
Digi Remote Manager® provides the remote management solution needed to monitor the components of the IoT device deployment, which may include a range of radio devices, system on modules (SOMs) and sensors.
Applications in this arena are varied. Lets look at three Digi customer stories for examples.

U.S. Water, which provides water treatment solutions to industrial clients across North America, turned to an IoT solution from Digi to establish a remote monitoring and management solution, in place of their current system. The goal was to improve visibility into field equipment installed at client sites. The organization has nearly 300 connected controllers and sensors at remote sites, which they wanted to connect into a complete solution.
U.S. water worked with Digi and Verizon to develop a solution using Digi cellular gateways and
XBee Zigbee sensors. Remotely connecting assets gives U.S. Water direct visibility to their equipment and to the customers usage of chemicals, as well as insight into their supply chain. The solution has helped U.S. Water create supply chain efficiencies and reduce transportation costs, since there are fewer truck rolls and technicians on the road.
 Summit Envirosolutions
Summit Envirosolutions is an environmental consulting firm that uses sophisticated information systems to gather and evaluate critical environmental data such as groundwater analytics and provide recommendations to their clients.
Summit's use case required a solution that streamlined their data collection processes. For example, instead of sending personnel to dozens of remote locations to perform tests and gather data, the team wanted to put automation to work, both to reduce the cost of unnecessary truck rolls and increase efficiency by eliminating the process of keying in the gathered data.
The solution involved integrating measurement sensors with battery-operated
Digi Connect® Sensor+ devices in the field to connect the data gathering system to the central servers. Automatically routing data to the servers from far-flung sensors saved time and money, and the solution included a method for capturing sensor diagnostics which enables the technicians to remotely diagnose the health of their sensors as well.
Air Force Civil Engineer Center (AFCEC)
is responsible for a range of programs, including the Air Force compliance, restoration, sustainability and National Environmental Policy Act programs.
Tasked with the environmental cleanup of the Superfund site at Joint Base Cape Cod (JBCC), the AFCEC team has been continuously remediating billions of gallons of contaminated water at the site over several decades. This process requires careful monitoring of over 100 source areas across the 22,000-acre restoration site.
The AFCEC team sought to reduce maintenance problems and costs, as the systems in place utilized landlines which were expensive to maintain. They worked with Digi and Verizon to develop a solution to convert their copper-wire landline installation to a wireless deployment utilizing
Digi WR21 cellular routers. The team deployed two routers in a pilot installation, followed by full deployment, ensured the systems and processes were working correctly, and then began full deployment.
See more water management and wastewater management solution stories in our customer case studies.
IoT applications in smart cities are vast and growing. These example use cases provide an overview of the range of solutions being developed across a range of industries.